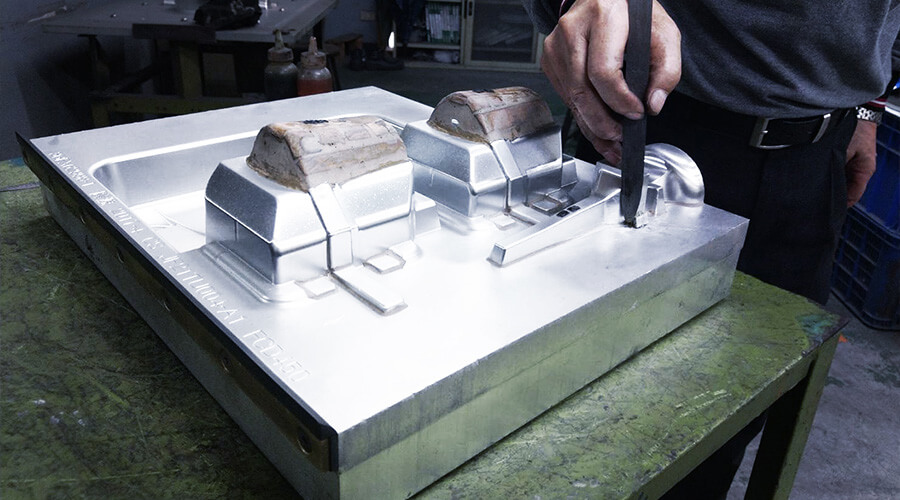
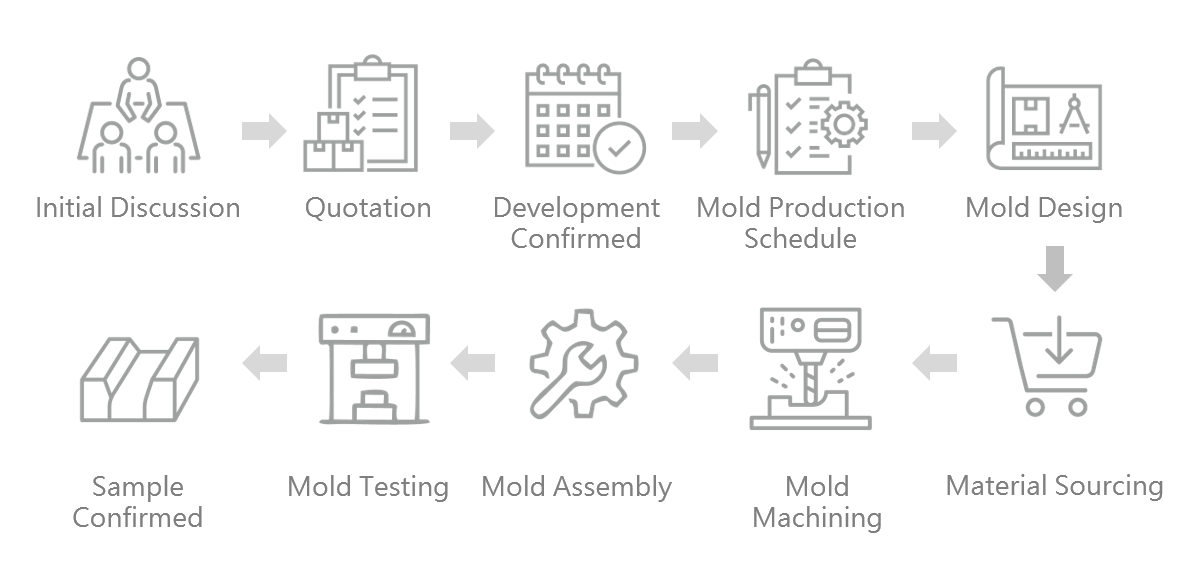
Precision Mold Design & Manufacturing for Mass Production
Metal forming has various processes and types such as casting, forging, extrusion, rolling, drawing, stamping, cutting, powder metallurgy, etc. Among all, the forming mold refers to the tool that allows the molten liquid metal with formability or fluidity to be injected or pressurized into the specified mold during the metal products forming process, and makes the metal into the specified shape. Mold has a specific contour or cavity shape, and the application of the cavity shape can make the metal material get a corresponding three-dimensional shape. Generally, Molds are made of a movable die and a fixed die. When molds are combined, the liquid metal is injected into the mold cavity to be formed, and the workpiece can be taken out when separated.
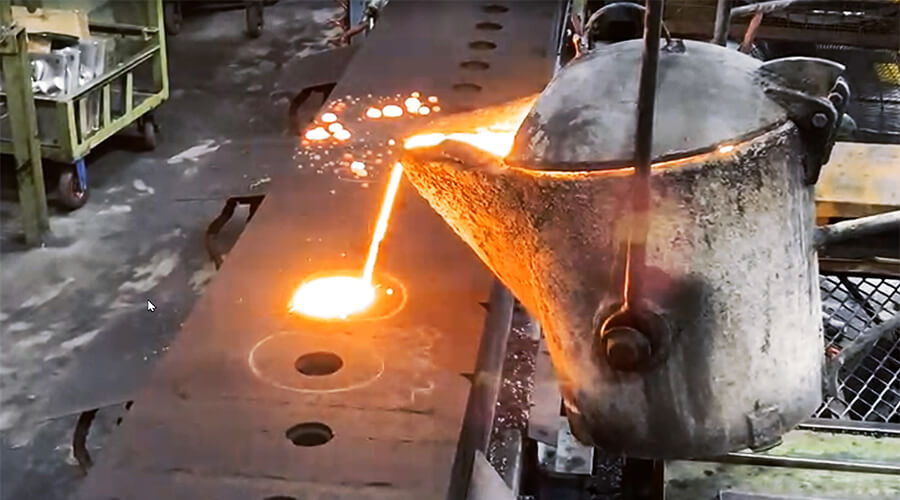

Extrusion dies can form metals precisely and quickly, especially for soft metals. For example, in the aluminum forming process, a strong pressure is applied to the aluminum placed in the mold cavity, forcing the aluminum to deform and extrude from the die hole of the extrusion die, to obtain the parts or semi-finished products with request cross-sectional shape or size.
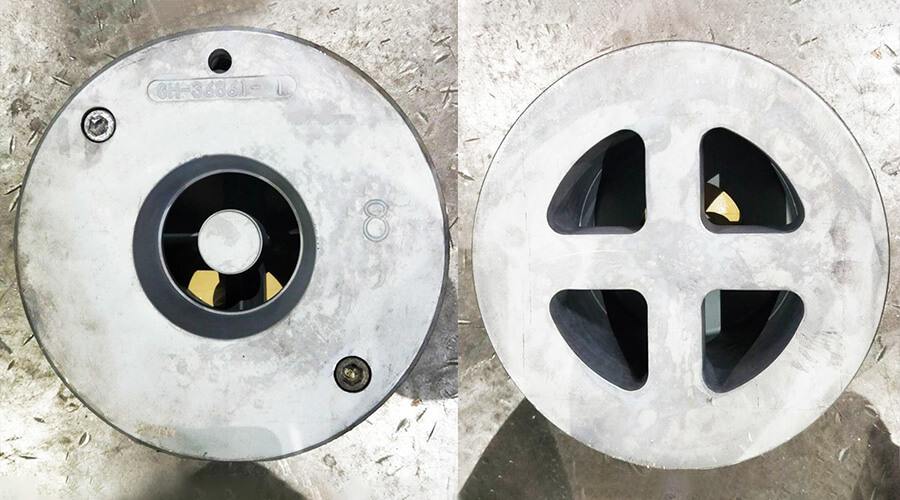
Die casting is a method of forming and solidifying under pressure to obtain castings. Die casting mold refers to a tool that holds molten metal under high speed, high pressure, and allows the metal to be filled and formed in the die casting cavity. Die casting has the advantages of high product precision, good cleanliness of surface, long life of die casting molds, high equipment performance, and saving post-machining and materials.
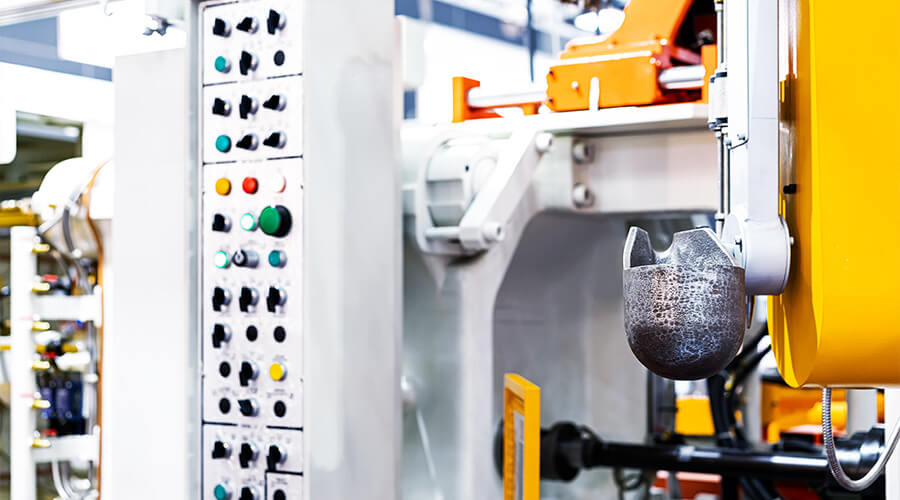

Gravity casting is a historical casting process. Molten metal is poured into a metal mold under gravity and cooled to form. Gravity casting molds are usually made of cast iron, carbon steel, graphite, copper or aluminum alloy, depending on the type of metal to be casted.
Molding is made of molding sand and core sand. During the sand casting process, molten metal is poured into the molding under gravity, and it will be cooled and formed without high pressure. After pouring and metal solidifying, open the mold and remove the sand from the hot casting, a sand casting is finished.
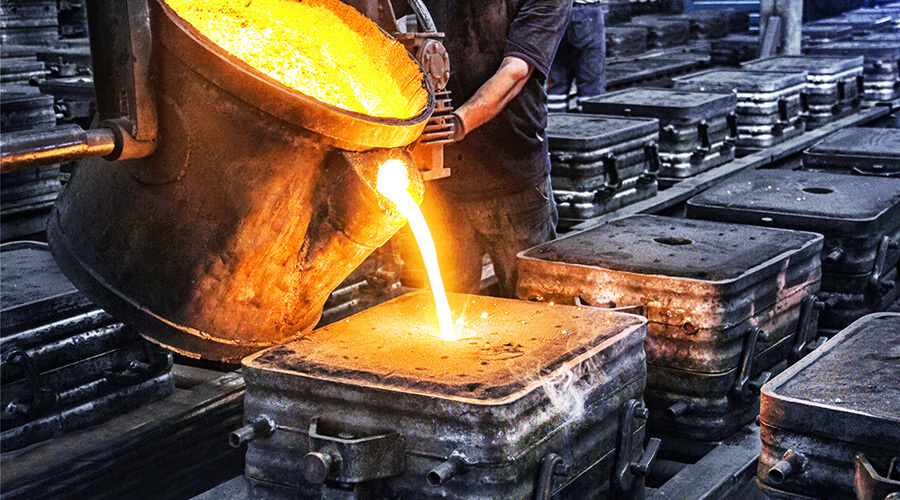

Refer to the die used in the forging process of small and medium metal parts. Through external force, metal material has plastic deformation in forging die, and then becomes the part in specific shape.
Forging die design determines the forming quality of precision metal parts. It is necessary to choose die material carefully, with heat treatment, advanced machining technology, to ensure the surface quality and precision of the die in the cavity.
At room temperature, pressure is applied to the material from a die mounted on the equipment, causing it in separation or plastic deformation, and then parts are finished.
In order to maintain the quality of the mold in future production, we will confirm the production record, the number of mold holes and the number of production times of each mold hole of the molds after production completed, and then put in storage as a basis for subsequent maintenance. Regular inspection and maintenance are required to ensure the availability of the molds after use for a certain number of molds, time or other specific standards.

