WKPT provides services ranging from metal material procurement, planning of mold, jigs and fixtures, CNC precision machining to surface treatment. On the metalworking production line, we use vertical and horizontal turning and milling machining centers to assist customers in solving the metalworking needs of high precision and complex metal parts. Our customers have benefited from our best machining solutions through the advantages of vertical and horizontal machining. We currently have more than 50 vertical and horizontal milling machining centers, CNC turning machines, and turning-milling centers, which can complete all the comprehensive machining processes at one time. Not only the current machining scale, we also continue to expand the machining center production line every year. In addition to the current high torque metalworking machines, we also expand the high-speed machining machines to strengthen the aluminum alloy high-precision machining capacity.
Surface treatment is the application of surface technology to metal components in order to strengthen the surface hardness or prolong the wear resistance and rust resistance of metal parts after the machining is completed. Surface treatment technology uses chemical or physical methods to form a single or multi-layer of protective materials with special properties on the surface, to increase the life of components and improve the appearance, properties and texture of products.
WKPT has integrated metalworking technologies from metal material forming, machining, surface treatment, assembly, welding and functional testing, etc. According to the needs of customized products, there are also corresponding manufacturing processes. In terms of assembly, there are dozens of operations involved, from the initial cleaning and protection to the final packaging. Assembly would be regarded as finished while all operations are implemented correctly on the standard operating procedure.
WKPT provides metal parts machining solutions including but not limited to machining. The machined metal parts sometimes need to be assembled with other parts into semi-finished products, and the assembly process of different parts is prone to errors. These errors not only happen in the machining process, but may also exist in the metal forming process. Therefore, after the semi-assembly process, a basic test on metal assembly parts must be carried out, and this process is called a function test.
Metal forming has various processes and types such as casting, forging, extrusion, rolling, drawing, stamping, cutting, powder metallurgy, etc. Among all, the forming mold refers to the tool that allows the molten liquid metal with formability or fluidity to be injected or pressurized into the specified mold during the metal products forming process, and makes the metal into the specified shape. Mold has a specific contour or cavity shape, and the application of the cavity shape can make the metal material get a corresponding three-dimensional shape. Generally, Molds are made of a movable die and a fixed die. When molds are combined, the liquid metal is injected into the mold cavity to be formed, and the workpiece can be taken out when separated.
During machining, when a metal workpiece is cut by a tool, the inertial force of the tool and machine will act on the workpiece itself.
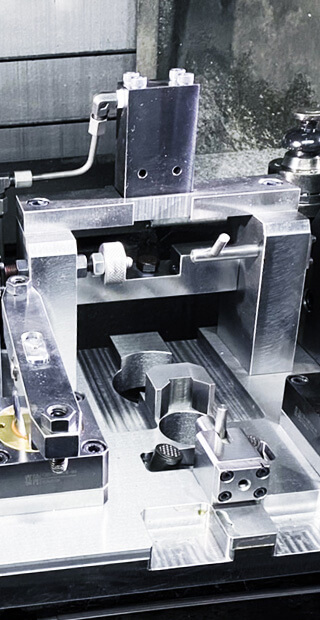
In order to keep the workpiece unmoved during the machining, a larger clamping force must be applied to stabilize the workpiece on the machine and absorb the cutting force to complete the cutting. The device that fixes and clamps the workpiece is called a fixture.
Compared with the fixture for a workpiece, the jig is a tool to guide the workpiece.
Especially when cutting on non-planar surfaces, the jig can position the tool precisely and stabilize the cutting. However, the CNC machining fixture of the machine can omit the guiding function of the tool; only the positioning and clamping functions are available.
Cast iron materials refer to iron-carbon alloys with carbon content more than 2.11%. In addition to carbon, there are also elements such as silicon, manganese, and a small amount of sulfur and phosphorus. Cast iron is usually made of pig iron, scrap steel, ferroalloys, etc. in different proportions through smelting. It has good performance in features such as casting, shock absorbing, pressure resistance, wear resistance, cutting processing, etc. Compared with other metal materials, cast iron production equipment and technology are relatively simple and low in price, so it is widely used in machinery manufacturing, petroleum, chemical industry, metallurgy, transportation and military industries, etc. Industrial cast iron generally contains 2.5% to 3.5% carbon. Carbon mostly presents in the form of graphite in cast iron. Based on the form of graphite, it can be roughly divided into white cast iron (steel-making pig iron), gray cast iron, malleable cast iron, ductile iron, etc.
WKPT utilizes multi-axis milling machines, machining centers, CNC machine tools, and grinders to manufacture high-precision, lightweight aluminum alloy parts to meet the manufacturing needs of vehicles, power machinery, and other components. Aluminum alloys offer low density but high strength, approaching or exceeding that of high-quality steel. They also possess excellent plasticity, can be processed into various profiles, and possess superior electrical and thermal conductivity.
Stainless steel is a general term for high-alloy steels typically made from iron with 12% to 30% chromium and other alloying elements added. WKPT utilizes multi-axis milling machines, machining centers, digital machine tools, and grinders to manufacture high-precision stainless steel parts for vehicles, power machinery, and other applications.
WKPT uses multi-axis milling machines, machining centers, CNC machine tools and grinders to manufacture high-precision carbon steel parts to meet the needs of vehicles, power machinery and other industrial parts.